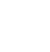
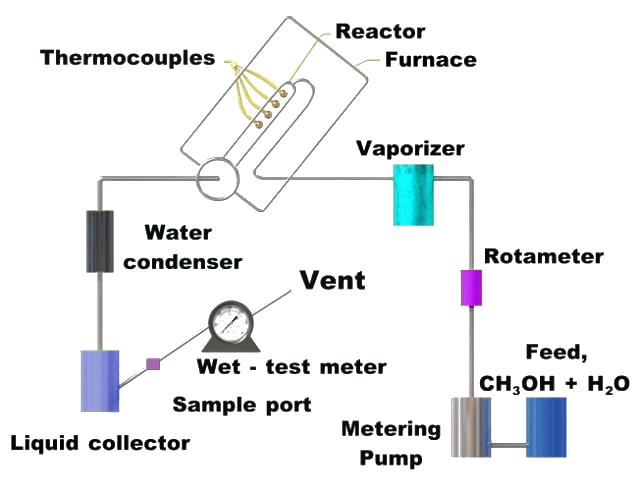
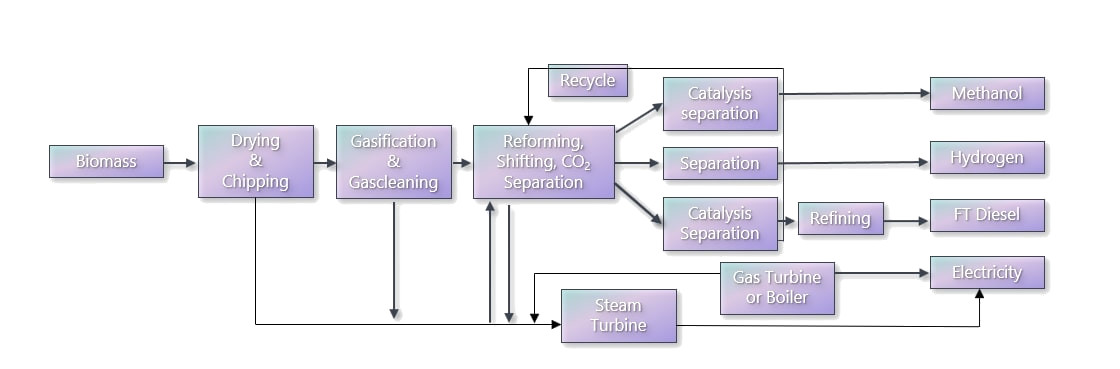
Carbon dioxide is a major exhaust in any production of hydrogen from fossil fuels. The amount of CO2 varies depending on the hydrogen content of the starting material. In order to achieve sustainable (emission-free) production of hydrogen, the CO2 should be captured and stored. This process is known as decarbonization. There are three (3) different ways to capture CO2 in a combustion process:
1. the afterburning. The CO2 can be removed from the exhaust gas of the combustion process in a conventional steam turbine or a combined cycle power plant (gas and steam turbine power plant). This can be done via the “amine” process, for example. In addition to water vapor, CO2 and CO, the exhaust gas will contain large amounts of nitrogen and some amounts of nitrogen oxides.
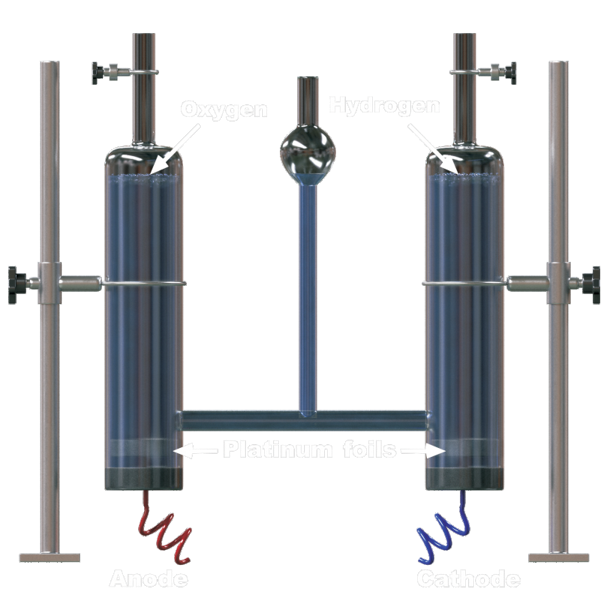
2. Pre-combustion. During the production of hydrogen, CO2 is captured using one of the processes described above.
3. Oxyfuel combustion. The fossil fuel is converted into heat in a combustion process using a conventional steam turbine or CCGT power plant. This is done with pure oxygen as the oxidizing agent. Usually, CO2 and water vapor are formed in the exhaust gas or in the flue gases, and CO2 can be easily separated by condensation of the water vapor.
In post-combustion and oxyfuel combustion systems, electricity is turned into near-conventional steam and combined cycle power plants. The electricity generated could then be used for water electrolysis.
If CO2 is captured and stored in an energy conversion process with relatively low efficiency and the electricity is used to electrolyze water, then the overall efficiency from fuel to hydrogen would not exceed 30%.
The captured CO2 can be found in geological formations such as oil and gas fields as well as in aquifers, but the feasibility and evidence of permanent CO2 storage are critical to the success of decarbonization.
The choice of the transport system for the CO2 (pipeline, ship or combined) will largely depend on the choice of the location of the production facility and the location chosen for storage.